Kartoza - How to get GIS going at your school
GIS is the exciting world of modern and applied geography. It can seem overwhelming to implement GIS in your school curriculum. This is a one-stop teacher's guide to getting GIS going in your classroo
This post guides geography teachers seeking to implement GIS software as part of the teaching curriculum. GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, are vital to real-world map making, spatial problem-solving, and spatial data visualisation. We discuss GIS software, documentation and data resources.
GIS Software
Don't let GIS software costs put you off teaching GIS at school. There are zero licence costs with free and open-source technology like QGIS, Mergin Maps and QField. There's also lots of free and open data around. QGIS runs on any desktop or notebook computer, even on older technology. Mergin Maps and QField run on smartphones and tablets.
Pro tip!: Get your students to install the software and run with it themselves - they will figure it out and teach you!
QGIS
QGIS is a free and open source desktop GIS that allows users to create, edit, visualise, analyse and publish geospatial information. QGIS is a full-featured GIS for which there are many free online resources. Further, there is a vibrant community of QGIS users, developers, and documenters that can be drawn on for advice and knowledge.
Two versions (releases) of QGIS are available for download from the QGIS website. See how. The long-term release (LTR) is more stable, but lacks some of the newest functionality. The current release has the latest functionality, but may be slightly less stable than the LTR. QGIS is available for Windows, macOS and Linux. Ensure that users have permission to install software on their computers. You can install it on staff, student and school computers, there's no limit!
Mobile GIS
There are mobile GIS apps that allow the user to make layers and capture points, lines, polygons and attributes directly from a phone or tablet. These work best as a field data collection tool in conjunction with a QGIS desktop project. However, on their own, they can show the basic concepts of a GIS to learners.
Mergin Maps
Mergin Maps is a mobile version of QGIS. While it is mainly a survey tool to be used in conjunction with QGIS desktop, it can be used in isolation to make a project and collect data. This is useful to show the basic concepts of a GIS to students, like layers and the different data types, when they don't have access to a computer. Mergin Maps offers a cloud service for easy sharing of QGIS projects, forms and data. Visit their website to learn more.
QField is a similar alternative to Mergin Maps, also based on QGIS.
Getting help
Now that the GIS software options are covered, let's look at stable and mature resources you can use as the basis of your teaching material or as a learning reference. The QGIS user guide provides easy-to-follow tutorials and exercises to help you navigate the user interface and more. This documentation will walk you step by step through how QGIS works and how you can leverage the great features of the software to teach GIS in your class.
In addition to browsing the material at your discretion, there are several in-person and online courses available. If you want a curated GIS course created by teachers for teachers in South Africa, see Introduction to GIS in the Classroom, which covers lessons to use in the classroom from intermediate to senior and FET phase.
Getting maps and data
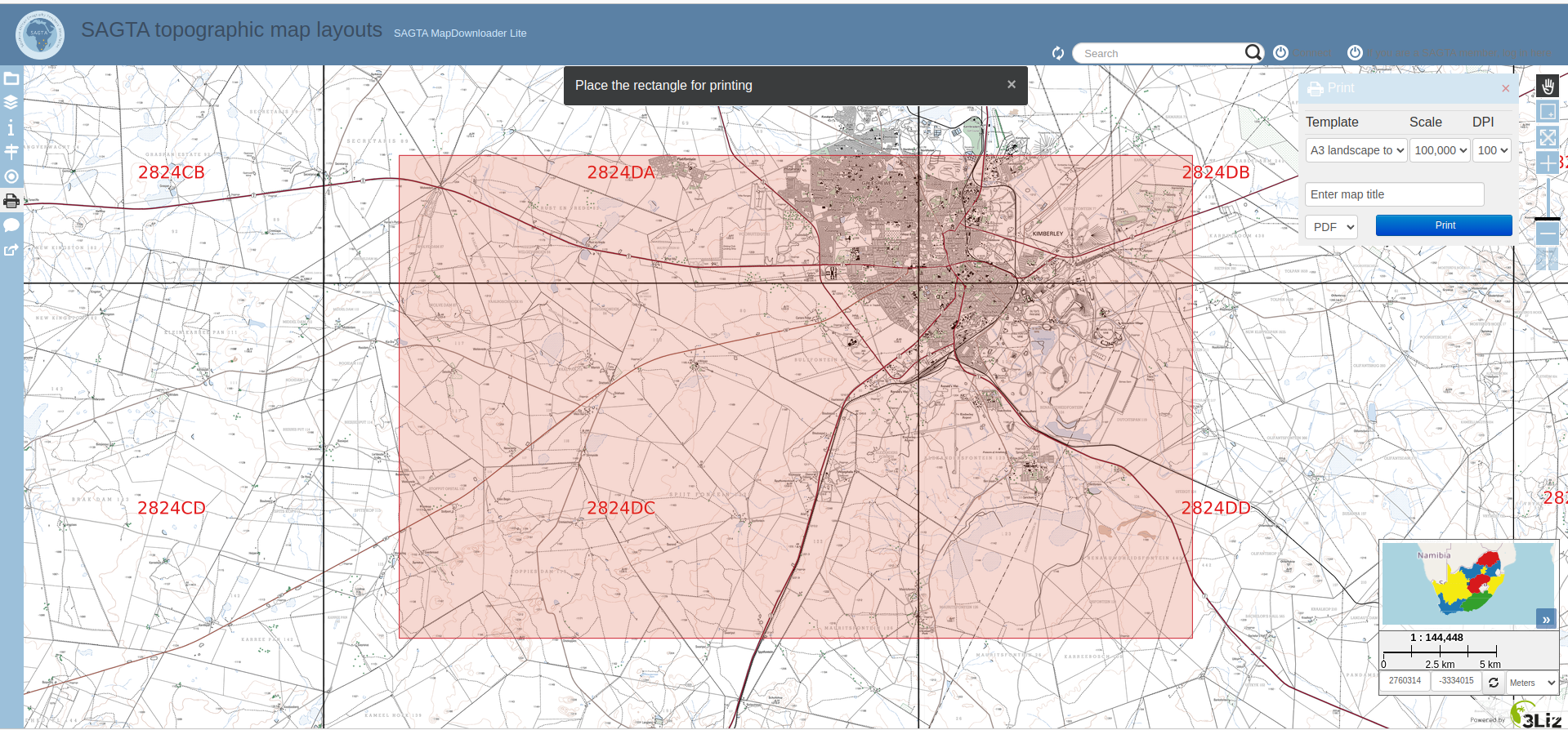
The SAGTA Map Downloader is an excellent tool that teachers and students can use in class for mapping exercises and assessments. We recommend you sign up with SAGTA (Southern African Geography Teachers' Association) to become part of a network of teachers who are there to support and give guided and full access to southern Africa’s best topographic, orthophoto and hybrid map downloader.
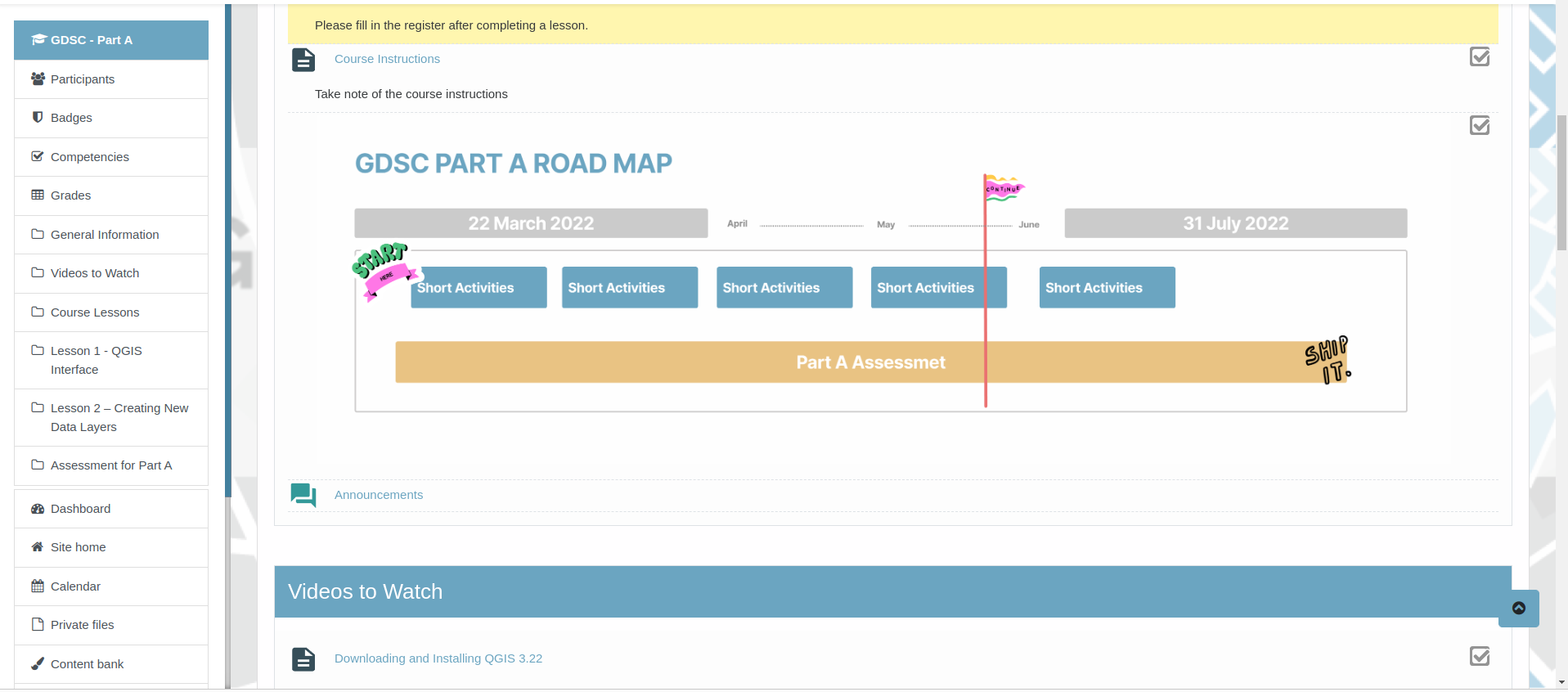
For students who are passionate about Geography and GIS the Geospatial Data Science Certificate (GDSC) is a fantastic option. The GDSC gives students ptractical experience with GIS beyond the geography curriculum. The growing programme was piloted by the IEB (Independent Examination Board) in 2022 but is open to all southern African students. It is supported by the University of Pretoria, SAGTA and Kartoza.
Vector data
OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a global Open Data platform that anyone can contribute to and obtain data from. It contains vector data such as roads, rivers, points of interest and land use. The data can easily be pulled into QGIS using a plugin like QuickOSM.
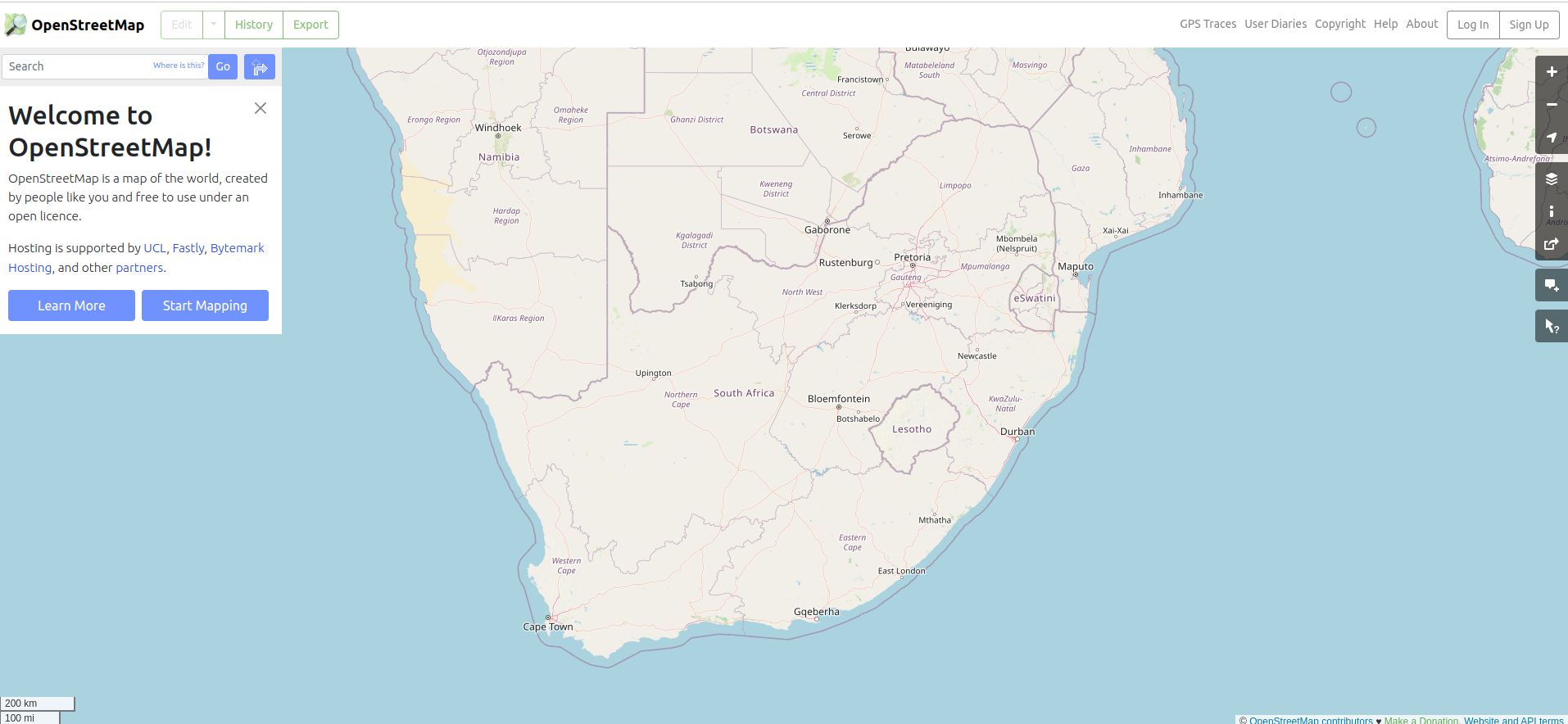
Anyone can create an account on OSM and capture data. It is a great resource for students to learn GIS by mapping their own neighbourhoods or schools. You can get students involved in mapping for good by contributing to the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT)
Raster Data
NASA is one of many services that provide Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and satellite remotely sensed images for free by just signing up for an account. QGIS has some plugins that help you download such data directly, such as the SRTM-downloader or Sentinel-2 downloader. These are awesome for showing students how to work with raster data and visualise elevation data and imagery.
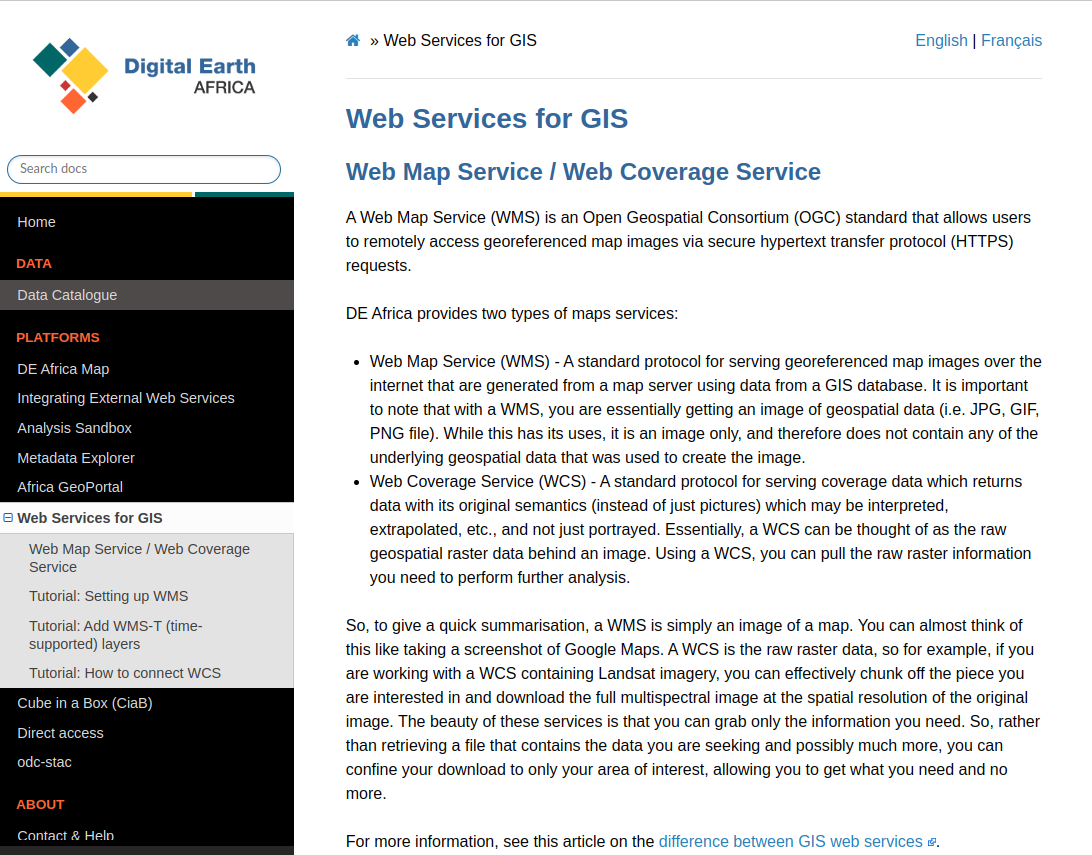
Digital Earth Africa (DEA) provides different raster data layers, including aerial imagery, water and flooding data and temperature data. DEA has a good quality catalog and documentation on how to connect their Web Map Service (WMS) to QGIS and easily access the data.

No comments yet. Login to start a new discussion Start a new discussion