Kartoza - Using WMS-T layers with QGIS Temporal Controller
The Temporal controller has added the ability for users to access and visualise WMS-T data in QGIS. Users can now load and analyse all varieties of WMS-T layers in QGIS.
The FOSS4G 2022 conference was held in Firenze, Italy, from 22th to 27th August. It was the first in person conference since the COVID outbreak.
Thanks to the organisers for making it possible and kudos to all the people that were involved in the preparation and the conducting of the conference.
I got a chance to attend and to present in the conference. It was a wonderful trip from the moment I started my flight from Dar es Salaam to Rome up to when I met other FOSS4G attendees in Florence. The conference allowed us to get acquainted with people that came from different parts of the world and to spend time in person with people that for some of us we only met and worked with virtually. This resulted into a joyful experience that left a huge memorable mark.
The conference provided a platform for sharing, learning and raising awareness about the Free and Open Source Software that exists in the Geospatial spectrum. One of the realizations I had during the conference is that a lot of the work that we are doing at Kartoza has a big influence in the FOSS Geospatial world. This confirms that we are a part of a group that is setting standards on how to develop, train and provide software development services using diverse teams that work remotely across the world.
As one of participants that were selected to give presentations at the conference. I delivered presentations about two topics that we have been working on here at Kartoza. One was the QGIS STAC API plugin and another was the QGIS temporal controller with WMS-T layers.
In this post I'm going to share about the QGIS temporal controller with WMS-T layers topic. Since the release of the Temporal Controller in the QGIS
application, most people have been aware more about the usage of the Temporal Controller with temporal vector data; there is not much coverage about
the other types of data that can also be used with the QGIS Temporal controller, including WMS temporal data. This was the drive that made me propose this presentation to the FOSS4G organisers; there hasn't been enough material about usage of WMS-T layers with the QGIS Temporal Controller.
The QGIS Temporal Controller is a framework that enables QGIS to deal with, manage and visualise temporal data. Before the Temporal Controller, QGIS had no core support for temporal data; users had to install plugins to manage temporal data. One of the plugins that provided temporal capabilities to QGIS
was the Time Manager plugin written by Anita Graser, which had more than a hundred thousand downloads. It had support for various data including PostGIS layers, vector layers and Spatialite layers.
Some of the challenges the QGIS temporal related plugins had were: It was hard for them to include functionality to cover all types of QGIS temporal layers because of some core features being inaccessible, a consequence of QGIS core structure and design; the first challenge had led to a situation where we would possibly need one plugin for each temporal data type in QGIS, which would result in a plethora of QGIS temporal related plugins.
The QGIS Temporal Controller solves all of the mentioned challenges. It contains a core API that all the QGIS data providers can use to add temporal support for their respective data. Because of this API it is now possible to manage, visualise and perform animation of all the QGIS temporal data as layers at once. This means users can open a vector layer, PostGIS layer and raster layer that have temporal properties and visualise them together in a single QGIS map canvas.
The work for making the Temporal Controller started in 2019 and was done by Kartoza in collaboration with North Road funded by the Canadian government under a MapGears contract. The Temporal Controller was released in the QGIS 3.14 version. The Temporal Controller implementation is all in core, which makes it very powerful, with strong perfomance, and it touches many QGIS areas including layouts, projects, expressions and other parts.
The Temporal Controller contains a lot of features and will require separate posts to cover all of them. The scope of this blog is for WMS-T support, hence we won't discuss more about the Temporal Controller features, rather the usage of WMS-T with the Temporal Controller.
WMS layers are supported inside QGIS through the WMS data provider. Users can browse WMS services and load their map layers inside QGIS. Below is a screenshot of how to load WMS layers into QGIS using the Browser panel.
The WMS specification allows serving of layers that have temporal properties. Users can use QGIS to fetch the layers that such services provide, along with their advertised time capabilities. Once a WMS service is added as a connection and the user loads the corresponding temporal layer from it, the Layer properties' "Temporal" tab can be used to query the available temporal layer data.
Below is the screenshot of the "Temporal" tab, showing layer temporal controller and the WMS-T settings.
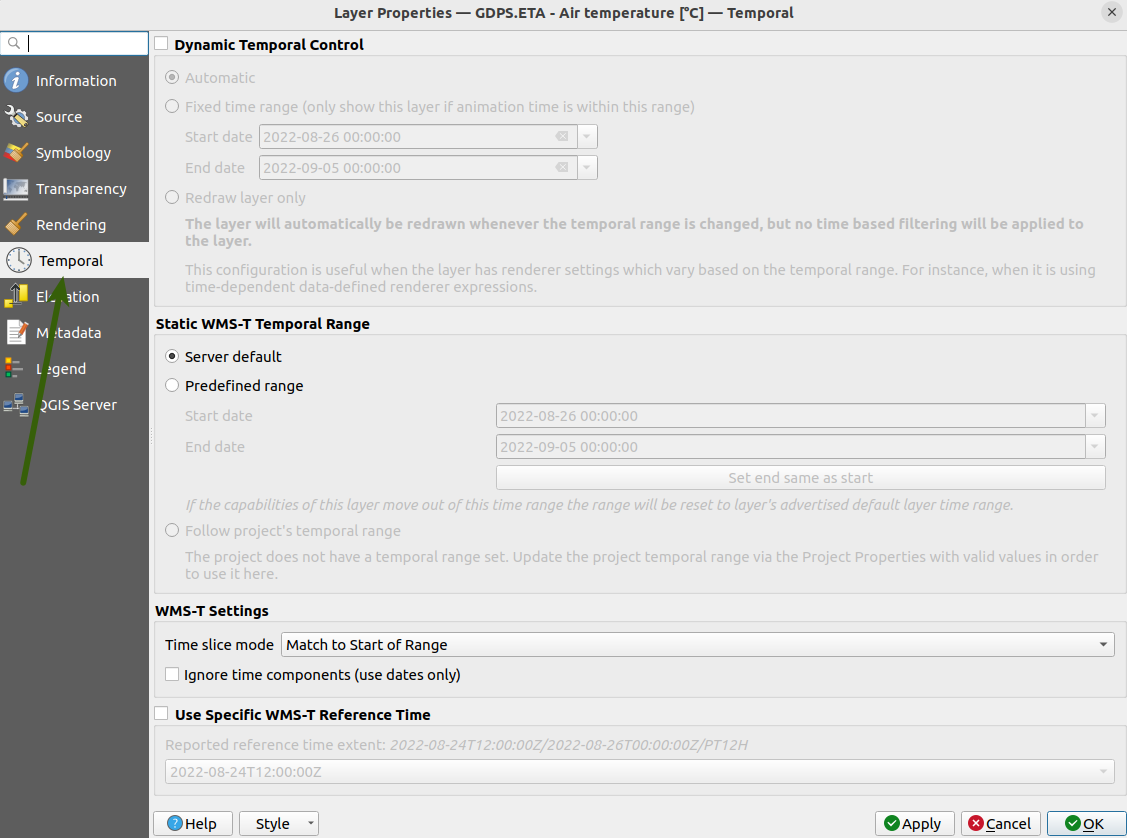
The WMS-T settings are only shown in the temporal tab if the layer is a WMS-T layer. Once the tab is open, the option "Dynamic Temporal Control" will be checked if the QGIS Temporal controller is active on the current layer. If it is deactivated, the option will be unchecked.
The "Static WMS-T Temporal Range" group contain settings that enable the user to set and fetch a specific temporal range data from the layer. Below are the available options and their descriptions:
- Server default
This option is the default selected option; when it is chosen, the layer will use its service default temporal range data
- Predefined range
Users can manually enter the dates that they want to be in the targeted temporal range
- Project temporal range
The project temporal range option allow users to select the current QGIS project temporal range to be used in the selected WMS-T layer;
this option will be disabled if the QGIS project temporal range is not set or it doesn't contain valid values.
Users are able to access the "Static WMS-T Temporal Range" settings only when the "Dynamic Temporal Control" is deactivated otherwise these settings will
be disabled.
Below the "Static WMS-T Temporal Range" there is a "WMS-T settings" group which is responsible for specifying how the applied temporal range is formatted before it is sent to the layer service for the data request. The "Time slice mode" option is used to set how the passed temporal range should be treated
e.g. a temporal range with value 01/01/2023 - 02/02/2023 will be passed on as 01/01/2023 - 01/01/2023 if a "Match to Start of Range" mode is selected.
For Bi-temporal WMS-T layers the "Use Specific WMS-T Reference Time" option is used to select the reference time from a list of the available reference times. This is useful for services that provide temporal data via WMS that make use of a reference time.
Example WMS-T layer inside QGIS; the layer shows the global air temperature prediction by the Canadian Weather service
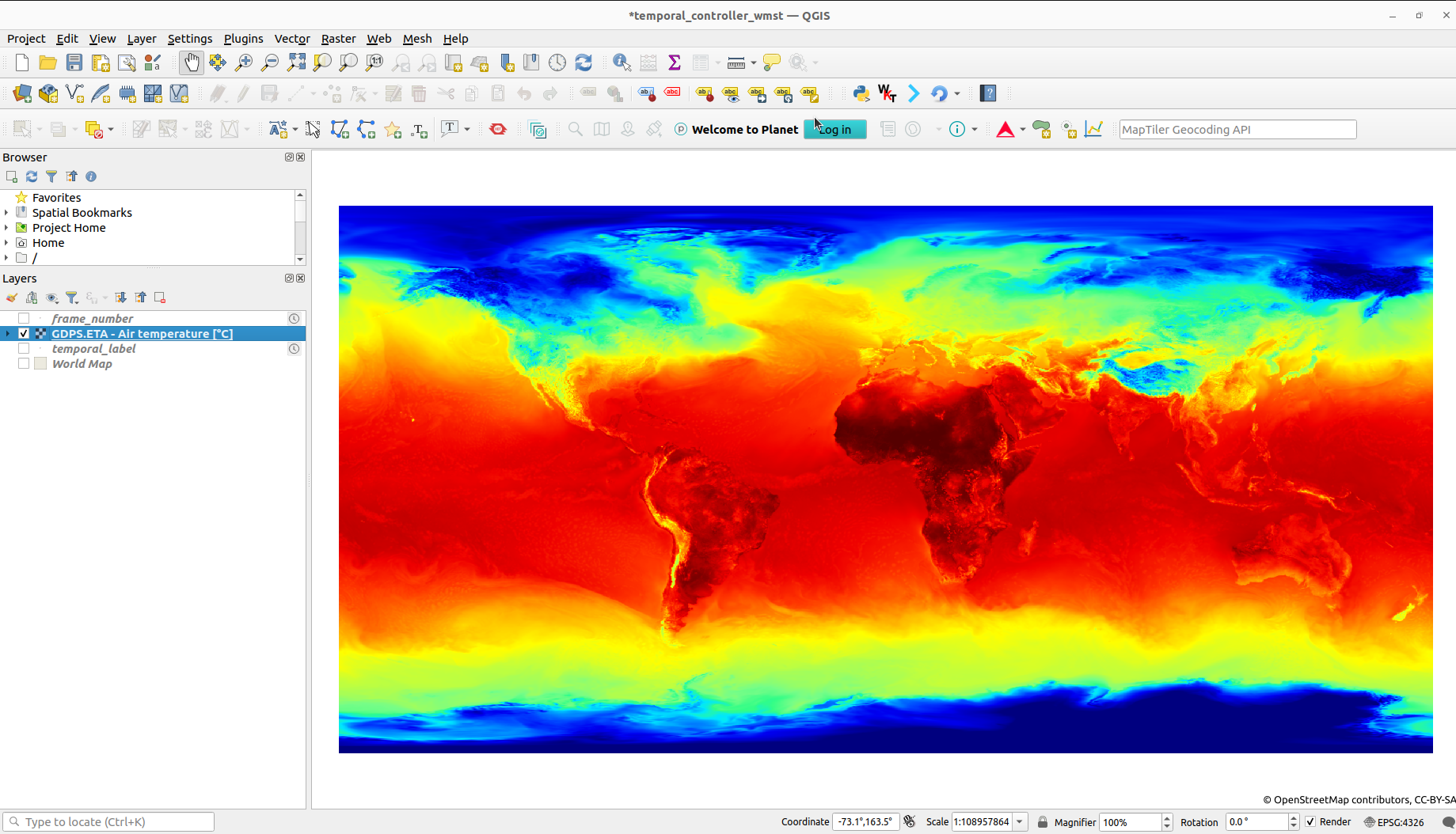
Users can use the QGIS Temporal controller easily to visualise WMS-T layer data across a large temporal range, because the Temporal controller provides
animation widgets that enable simple navigation for the different temporal ranges. The Temporal controller contains a slider and a couple of control buttons that can be used to update the WMS-T layer's temporal range and hence fetch data for the provided temporal range.
From this ability, users are now able to create different types of animation by using the QGIS Temporal controller together with the WMS-T layers.
Screenshot of animation of wind direction using a WMS-T layer from Meteorologic Service of Canada.
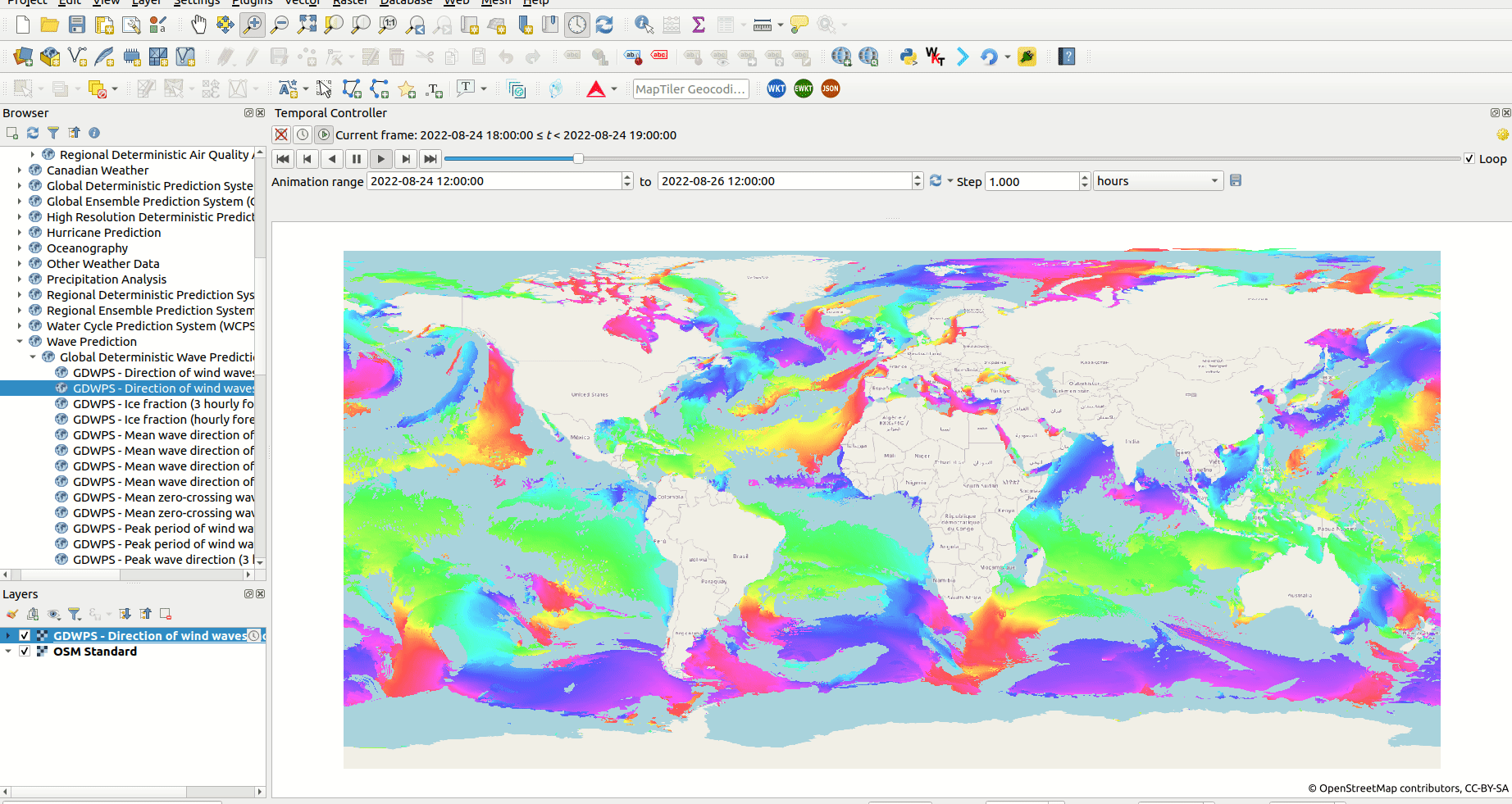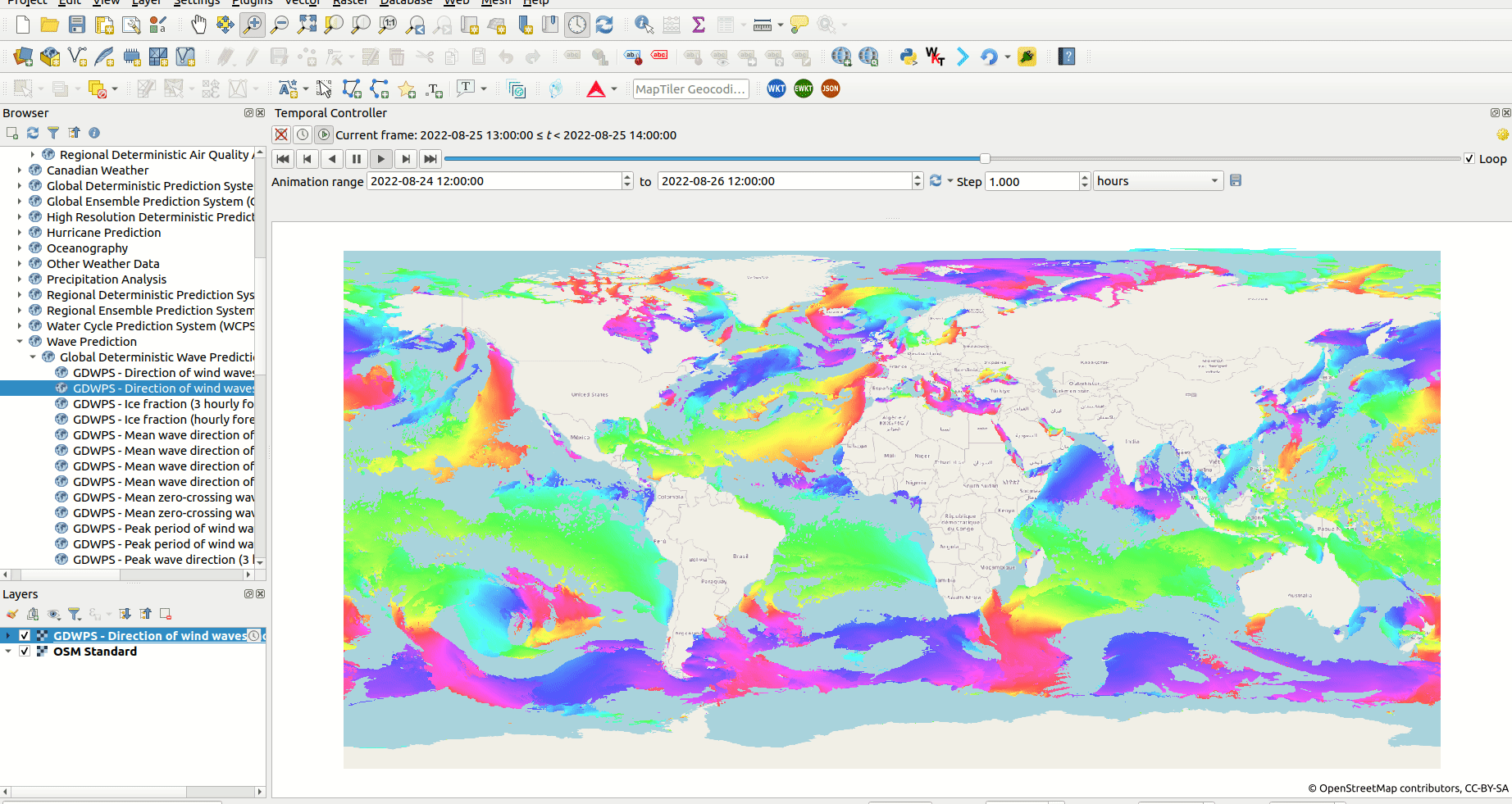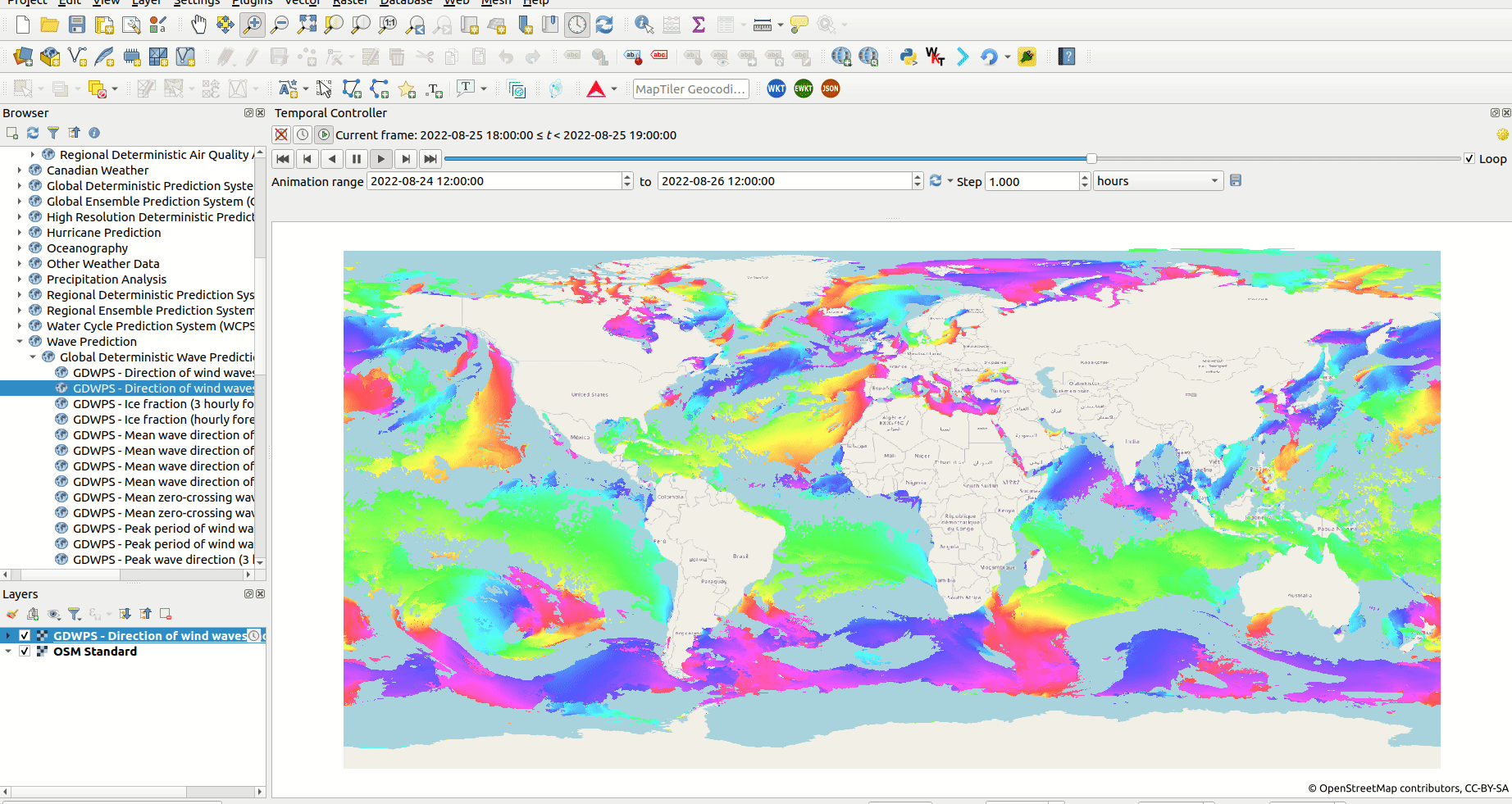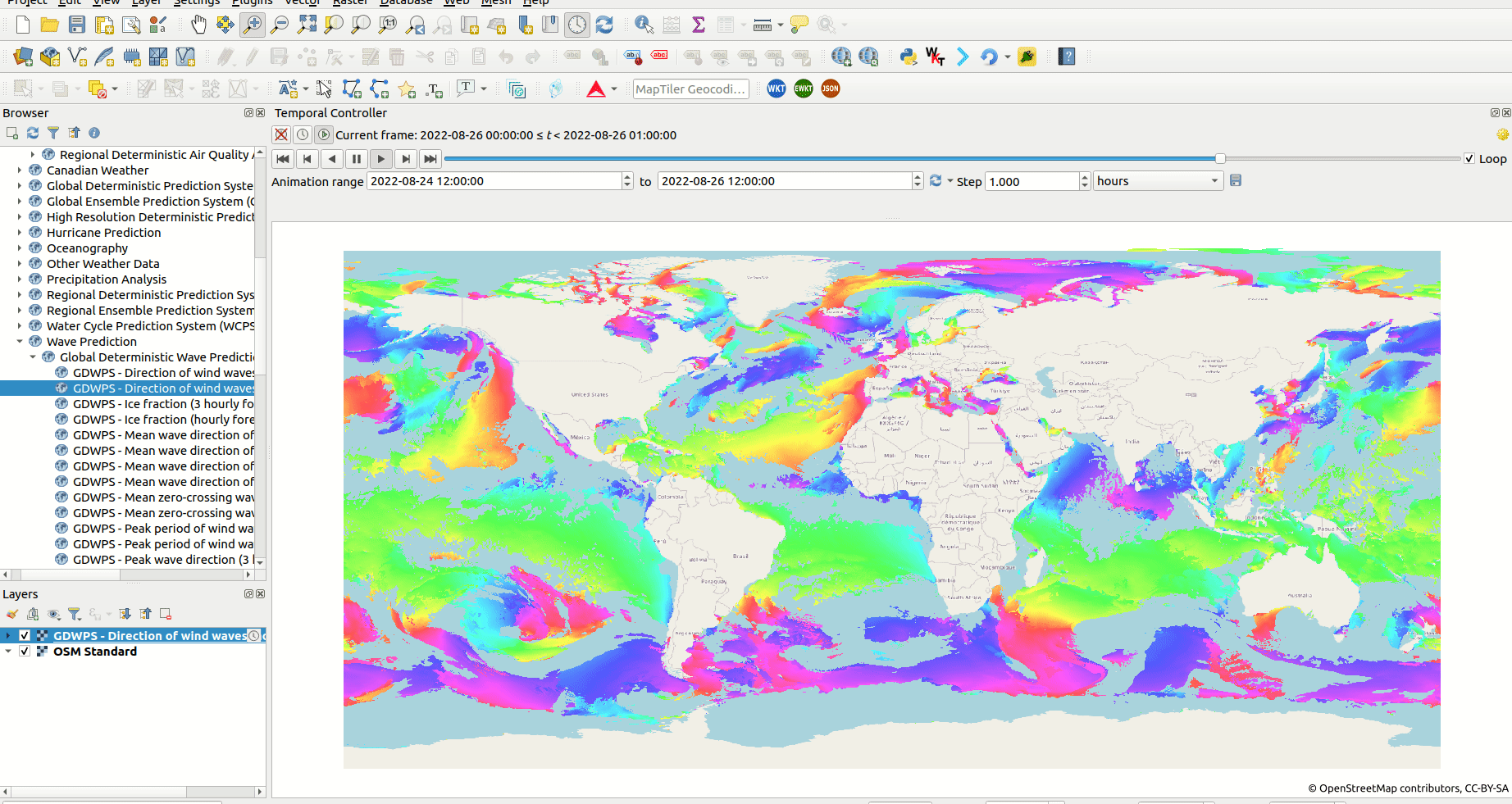
The Temporal controller has added the ability for users to access and visualise WMS-T data in QGIS. Users can now load and analyse all varieties of
WMS-T layers in QGIS. Also, through the QGIS Python API, developers can tap in and develop Python applications that use the Temporal controller
functionality.
Notes:
If you have any issues or questions when using the QGIS Temporal controller please visit https://github.com/qgis/QGIS/issues
For more information about QGIS Temporal controller see Nyall's talk https://youtu.be/vgDg5cRwPRw?t=945

No comments yet. Login to start a new discussion Start a new discussion